Amire Comfort M.1,
E. O. Omoare2
1Crawford University Igbesa, Ogun State, Nigeria
2Ogun State Institute of Technology (OGITECH) Igbesa, Ogun State, Nigeria
Correspondence to: Amire Comfort M., Crawford University Igbesa, Ogun State, Nigeria.
| Email: |  |
Copyright © 2015 Scientific & Academic Publishing. All Rights Reserved.
Abstract
Economic activities can be described as legal
activities that create and distribute utility from points of production
to places of final consumption at a price. Economic activities have been
classified into productive activities, commercial activities,
distributive activities and service activities. Economic activities are
embarked on by two separate economic agents identified as suppliers and
buyers. The advent of money resulted into growth and development in
economic activities. However, negative consequences associated with
cash-based transactions necessitated the adoption of cashless policy.
The cashless policy is a policy that encourages more electronic-based
transactions. The aim of this study is to determine how some factors of
cashless policy impact on economic activities. Some of these factors are
availability of power, infrastructures and literacy level. Findings
revealed that cashless policy has contributed to the promotion of
technology enhanced businesses. In addition, constant and regular supply
of electricity will aid cashless policy, thereby strengthening economic
activities in Developing countries.
Keywords:
Cashless policy, Economic activities., Cash-based economy, Electronic-based transactions
Cite this paper: Amire Comfort M., E. O. Omoare, Cashless Policy and Economic Activities in Developing Countries (A Case Study of Nigeria),
American Journal of Economics, Vol. 5 No. 4, 2015, pp. 417-422. doi: 10.5923/j.economics.20150504.03.
1. Introduction
2. Objectives of the Study
3. Review of Literature and Theoretical Framework
4. Methodology
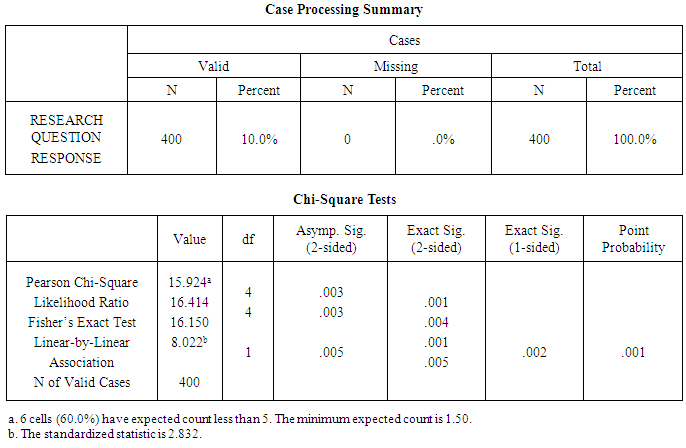
Table 1. Educational Qualification
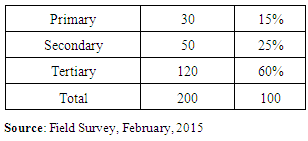 |
|
|
|
|
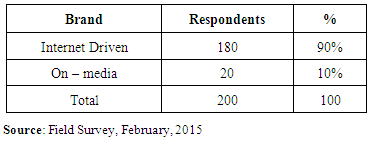
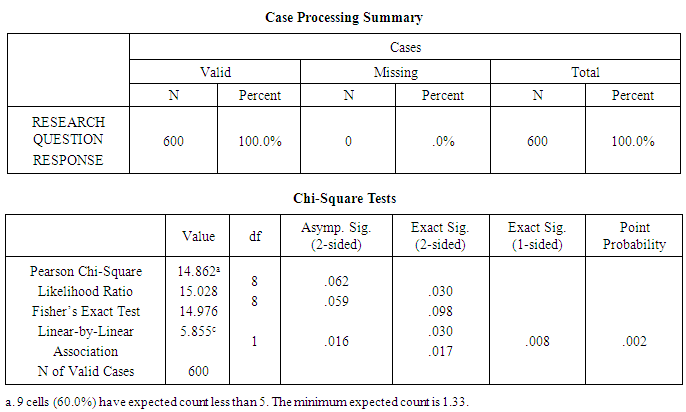
Table 2. Type of Phone Used
 |
|
|
|
|
5. Summary, Conclusions and Recommendations
References
| [1] | McConnel, C.R and Brue, C.L (1999) Economics: Principles, Problems and Policies Irwin McCraw-Hill USA. |
| [2] | Abiraj, B.M.C (1998) Higher Level Business and Economics for Caribbean Students Arnold Publishers Great Britain. |
| [3] | Miller, R.L (1996) Economics Today Harper Collins College Publishers New York. |
| [4] | Adekanye, F. (1983) The Elements of Banking in Nigeria F&A Publishers Ltd Lagos. |
| [5] | The Central Bank of Nigeria, (Cash-less Nigeria). Available at https://www.cenbank.org/cashless/ last visited on 6th of June 2015. |
| [6] | Hetzel,
R.L (1993) A Quantity Theory Framework for Monetary Policy Federal
Reserve Bank of Richmond Economic Quarterly Volume 7913 Summer 1993
www.google.com retrieved 20/2/2015. |
| [7] | Reem
Heakal, “what is the quantity theory of money”. Available
athttps://www.investopedia.com/articles/05/010705.asp last visited on
06/06/2015. |
| [8] | Folarin, F. (2014) Cashless Policy and Online Shopping: Matter Arising Sundiata Post www.google.com retrieved 20/2/2015. |
| [9] | Oginni,
S.O., El-Maudie, J. Gambo, M. Abba and M.E. Onuh (2013) Electronic
Payment System and Economic Growth. A Review of Transition to Cashless
Economy in Nigeria International Journal of Scientific Engineering and
Technology Volume No 2 Issue No 9 pp 903-913 ISSN:2277-1581
www.google.com retrieved 20/2/2015. |
| [10] | Waithaka
James Mwangi 2015, “The effect of GDP Re-basing in Kenya”. A
publication of the School of Economics, University of Nairobi. Available
at
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/274634051_THE_EFFECT_OF_GDP_RE_BASING_IN_kENYA
last visited on 06/06/2015. |








 Abstract
Abstract Reference
Reference Full-Text PDF
Full-Text PDF Full-text HTML
Full-text HTML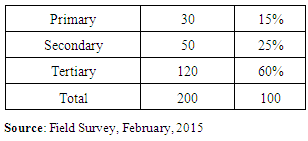

 About Blogindoor
About Blogindoor
No comments:
Post a Comment